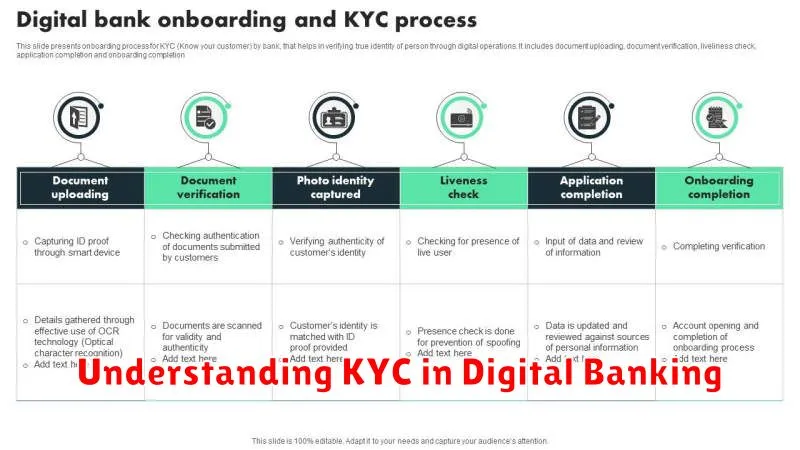
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, Know Your Customer (KYC) regulations play a crucial role in ensuring the security and integrity of digital banking. Understanding KYC is essential for both financial institutions and customers. For institutions, robust KYC procedures help mitigate risks associated with fraud, money laundering, and terrorist financing. For customers, understanding KYC helps build trust and ensures a safe and secure banking experience. This article will delve into the intricacies of KYC in digital banking, exploring its importance, processes, and impact on the financial ecosystem.
From identity verification to ongoing monitoring, KYC encompasses a range of processes designed to establish and maintain a customer’s identity and assess their risk profile. We will examine the various KYC checks employed by digital banks, including document verification, biometric authentication, and customer due diligence (CDD). Additionally, we will explore the challenges and opportunities presented by KYC in the context of digital banking, focusing on the balance between security, customer experience, and regulatory compliance. Join us as we unravel the key aspects of KYC in digital banking and its significance in shaping the future of finance.
What Is KYC?
KYC stands for Know Your Customer. It’s a set of procedures used by businesses, primarily financial institutions, to verify the identity of their clients. This process is crucial for preventing fraud, money laundering, and other illicit activities.
KYC involves collecting and verifying identifying information from customers. This information typically includes proof of identity, such as a government-issued ID card or passport, and proof of address, such as a utility bill or bank statement. The specific requirements may vary depending on the institution and the nature of the customer relationship.
The goal of KYC is to establish a customer’s true identity and assess the potential risks associated with doing business with them. By implementing robust KYC procedures, businesses can protect themselves from financial crime and maintain regulatory compliance.
Why KYC Is Mandatory
KYC, or Know Your Customer, is mandatory for several crucial reasons, primarily centered around mitigating risks and maintaining the integrity of the financial system.
Preventing Financial Crimes
Anti-money laundering (AML) and countering the financing of terrorism (CFT) are at the forefront of KYC requirements. By verifying customer identities and monitoring transactions, financial institutions can detect and prevent illicit activities, such as money laundering, terrorist financing, and fraud. This protects the institution and the broader financial system from exploitation.
Protecting Customers
KYC protocols help protect customers from identity theft and other fraudulent activities. By verifying identities, institutions can ensure that accounts are not opened fraudulently in a customer’s name.
Maintaining Financial Stability
Robust KYC practices contribute to the overall stability and integrity of the financial system by reducing the risk of criminal activity. This fosters trust and confidence in the banking sector.
Regulatory Compliance
Financial institutions are legally obligated to comply with KYC regulations established by governing bodies. These regulations are designed to prevent financial crimes and maintain the stability of the financial system. Non-compliance can result in significant penalties.
Documents Required
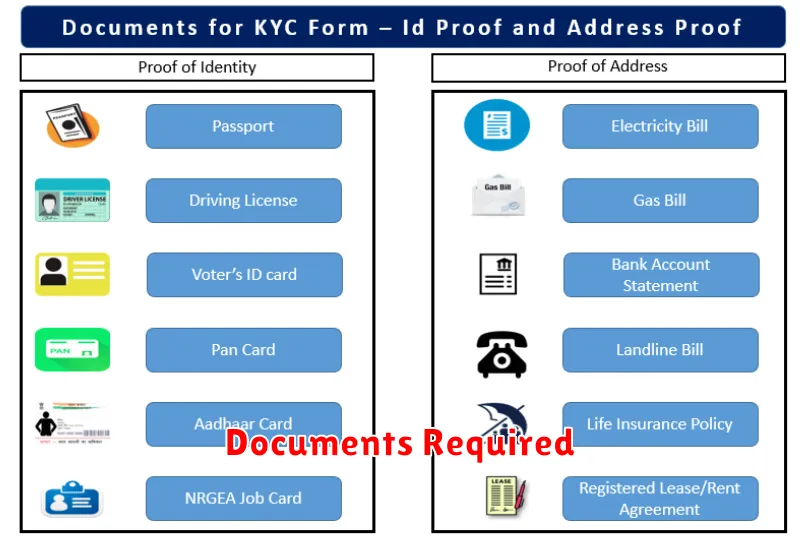
KYC procedures require specific documents to verify your identity. These documents typically fall into two categories: proof of identity and proof of address.
Proof of Identity
Acceptable forms of identification often include government-issued photo IDs such as a passport, driver’s license, or national identity card. Some institutions may also accept other official documents.
Proof of Address
Documents demonstrating your current residential address are essential. These can include utility bills (such as electricity or water bills), bank statements, or official government correspondence that displays your name and address.
The specific documents required may vary based on the institution and the jurisdiction. It is important to consult the digital bank’s specific KYC requirements to ensure you provide the correct documentation for a seamless verification process.
Verification Process Step-by-Step
The KYC verification process typically involves several key steps. Identity verification is the first step, where customers provide official identification documents like a passport or driver’s license. This information is then verified against official databases.
Address verification follows, often requiring proof of residence such as utility bills or bank statements. This confirms the customer’s declared address.
Biometric verification may also be required. This can involve facial recognition or fingerprint scanning, adding an extra layer of security and ensuring the person presenting the identification is the actual owner.
Finally, ongoing monitoring takes place. Financial institutions continuously monitor customer transactions and update KYC information periodically to ensure compliance and manage risk effectively.
Handling KYC Rejections
A KYC rejection can be frustrating, but it’s not necessarily the end of the road. Understanding the reason for rejection is the first step toward resolution. Financial institutions are required to provide you with a reason for the denial.
Common reasons for rejection include discrepancies in provided information, insufficient documentation, or flagged activity. Carefully review the rejection notice and identify the specific reason for denial. If the reason is unclear, contact the institution’s customer support for clarification.
Once you understand the reason, take the necessary steps to rectify the issue. This might involve providing additional documentation, correcting errors in your application, or addressing any security concerns. Ensure all information is accurate and up-to-date.
After addressing the issue, resubmit your KYC application. Be patient during the review process. If you continue to face issues, consider reaching out to the institution’s compliance department for further assistance.
How Digital Banks Simplify It
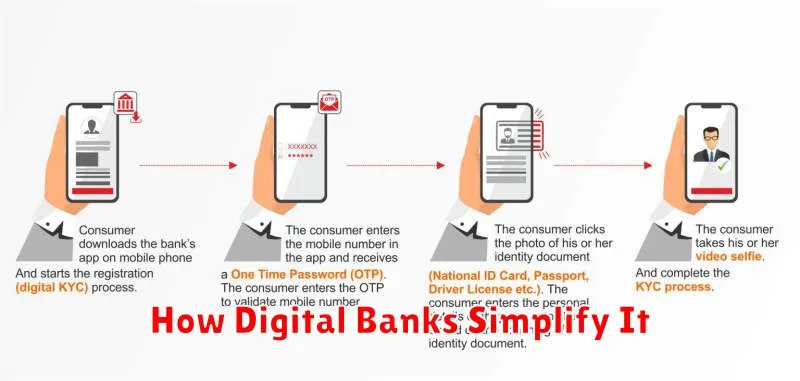
Digital banks leverage technology to streamline the KYC process, making it significantly more convenient for customers. They employ a variety of methods to achieve this simplification.
Digital Identity Verification
Automated systems verify customer identities through methods like facial recognition and document scanning. This eliminates the need for physical paperwork and in-person visits, saving customers valuable time and effort.
Real-time Updates
Dynamic KYC allows for ongoing monitoring of customer information. Changes in circumstances are tracked and updated automatically, reducing the need for repetitive documentation and ensuring compliance.
Centralized Data
Digital platforms allow for secure storage and access to customer data. This centralized approach simplifies information management for both the bank and the customer, enhancing efficiency and transparency.