Navigating the world of digital banking can be incredibly convenient, but it’s essential to understand the associated fees and charges. While digital banks often boast lower overhead than traditional institutions, they still have costs to cover. This comprehensive guide will delve into the common digital bank fees, including monthly maintenance fees, ATM fees, overdraft fees, foreign transaction fees, and other potential charges. Understanding these fees is crucial for choosing the right digital bank and maximizing your financial well-being.
From account maintenance fees to surprising hidden fees, this article aims to equip you with the knowledge you need to make informed decisions about your digital banking experience. We’ll explore the various fee structures, compare digital bank fees across different platforms, and provide valuable tips for minimizing or avoiding charges altogether. By understanding the potential costs associated with digital banking, you can select the best digital bank for your specific financial needs and avoid unexpected financial burdens. Let’s dive into the details of digital bank fees and charges.
What Fees to Expect
While digital banks often boast lower fees than traditional banks, it’s essential to understand what charges you might still encounter. Fees can vary significantly between institutions, so carefully review the fee schedule of any digital bank you’re considering.
Some common fees include monthly maintenance fees, though many digital banks waive these. You might also encounter excess transaction fees if you exceed a certain number of transactions per month. ATM fees, especially for using out-of-network ATMs, are another potential cost. While some digital banks offer reimbursements for these fees, others do not.
International transaction fees are common for purchases made in a foreign currency or with a foreign merchant. These fees can be a percentage of the transaction or a flat fee. Finally, be aware of potential inactivity fees if you don’t use your account regularly.
Monthly Maintenance Charges
Monthly maintenance charges are fees charged by digital banks for maintaining your account each month. These charges can vary depending on the bank and the type of account you hold. Some digital banks may waive these fees if you meet certain criteria, such as maintaining a minimum balance or having a recurring direct deposit.
It’s crucial to understand the monthly maintenance fee associated with your account to avoid unexpected deductions. Review the bank’s fee schedule or terms and conditions to find this information. Knowing this fee allows you to factor it into your budgeting and compare offerings from different digital banks.
Some banks offer tiered account options. Higher tier accounts may offer additional perks, but they may also come with higher monthly maintenance fees. Carefully consider your banking habits and needs when choosing an account to ensure you’re not paying for services you don’t use.
ATM Withdrawal Fees
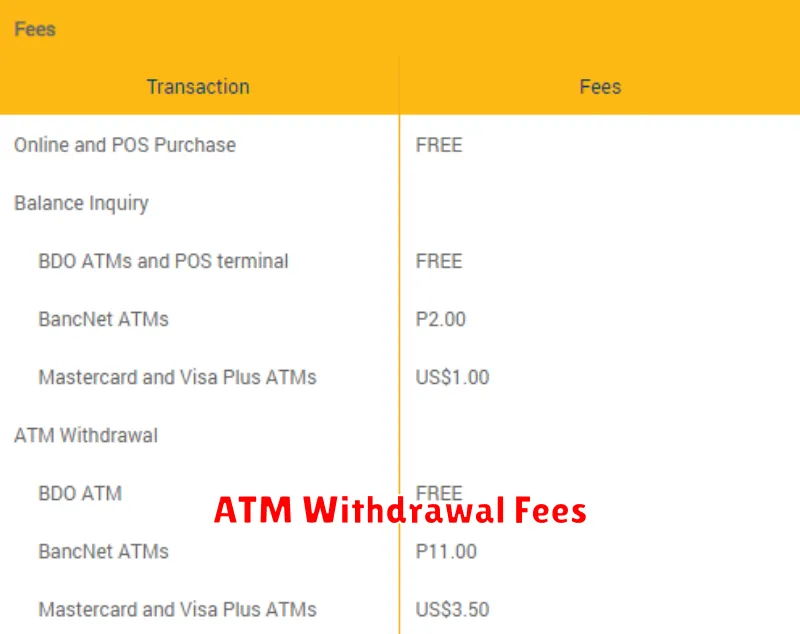
ATM withdrawal fees are charges incurred when you use your digital bank card to withdraw cash from an ATM. These fees can vary depending on several factors.
Types of ATM Withdrawal Fees
Out-of-Network ATM Fees: This is a common fee charged when you use an ATM not belonging to your digital bank’s network.
International ATM Fees: Withdrawing cash internationally often incurs additional fees. These can be a percentage of the withdrawal amount or a flat fee.
Digital Bank’s Own Fee: Some digital banks might charge their own fee for any ATM withdrawal, regardless of the ATM network.
Minimizing ATM Fees
Understanding your digital bank’s fee structure is crucial to avoid unnecessary charges. Look for digital banks with a large, surcharge-free ATM network or those that reimburse out-of-network ATM fees.
Foreign Transaction Costs
Foreign transaction costs are fees charged when you use your digital bank card for transactions in a currency other than your account’s base currency. These costs typically consist of two components.
1. Foreign Transaction Fee
This is a percentage-based fee, often ranging from 1% to 3%, added to the total transaction amount. The specific percentage depends on your digital bank’s fee schedule. This fee is charged by the bank for the currency conversion process.
2. Currency Exchange Markup
In addition to the transaction fee, a markup may be added to the exchange rate. This markup represents the difference between the mid-market exchange rate (the rate banks use among themselves) and the rate offered to you. This difference constitutes a profit for the bank. Be aware of this markup as it can impact the overall cost of your foreign transaction.
Carefully review your digital bank’s fee disclosure documents to understand their specific foreign transaction fees and how they handle currency exchange. Some banks offer premium accounts or cards with lower or no foreign transaction fees.
Hidden Charges to Watch
While digital banks often advertise lower fees, it’s crucial to be aware of potential hidden charges that can accumulate. Some institutions may impose fees for services not typically associated with traditional banks.
Inactivity Fees: If your account balance falls below a certain threshold or you don’t use your account regularly, some digital banks may charge an inactivity fee. Pay close attention to the terms and conditions regarding account usage to avoid these charges.
Excess Transaction Fees: Some digital banks limit the number of free transactions per month. Exceeding this limit may result in fees for each additional transaction. Be mindful of your transaction volume and choose an account that aligns with your banking habits.
International Transaction Fees: While some digital banks offer competitive exchange rates, be aware of potential foreign transaction fees or markup on currency conversions. Check the fee schedule for international transactions before using your card abroad.
Comparing Fee Structures
Fee structures vary significantly between digital banks. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the right bank for your needs. Some banks operate on a subscription model, charging a monthly or annual fee for premium services. This often comes with perks like higher interest rates or international transaction fee waivers.
Alternatively, many digital banks utilize a “freemium” model, offering basic services free of charge while charging fees for specific transactions or features. Common examples include fees for ATM withdrawals, international transfers, or early access to direct deposits.
Comparing these structures requires careful consideration of your banking habits. A high-volume user might benefit from a subscription model if the bundled services outweigh the recurring fee. Conversely, an infrequent user might prefer a freemium model to avoid unnecessary charges.
| Feature | Subscription Model | Freemium Model |
|---|---|---|
| Monthly Fee | Yes | No |
| ATM Fees | Potentially Waived | Usually Charged |
| International Transfers | Potentially Lower Fees | Usually Higher Fees |